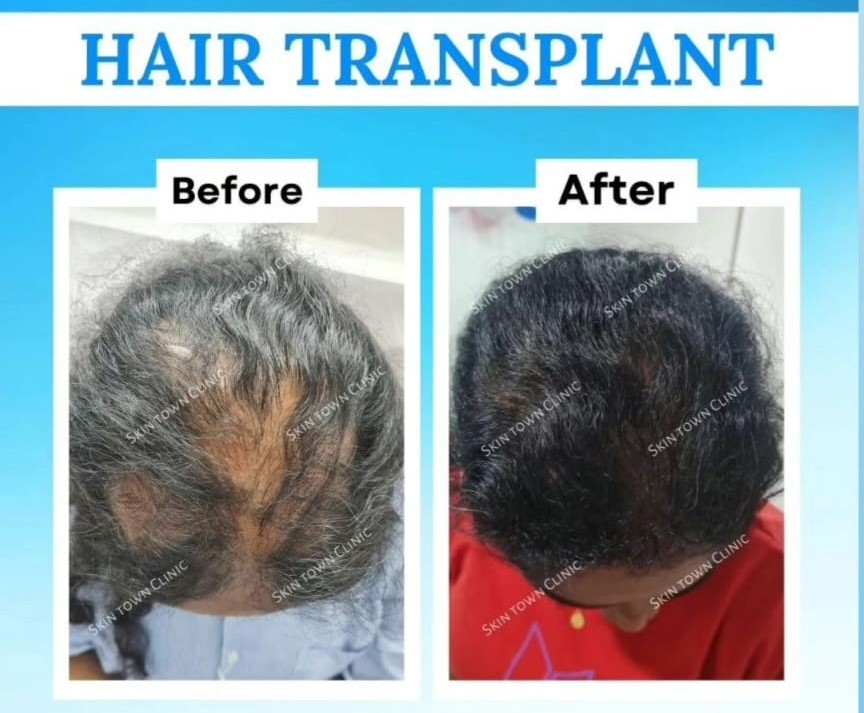
Hair loss can be a frustrating and emotional experience, affecting self-confidence and overall well-being. Alopecia, a condition that causes hair loss, affects millions of people worldwide, regardless of age or gender. For those struggling with hair loss, hair transplantation is often considered a promising solution. But is it the right option for every alopecia patient?
In this blog, we’ll take a closer look at how hair transplants work, which types of alopecia may benefit from them, and the factors to consider before opting for this procedure. With insights from dermatologists at SkinTown Clinic, we’ll help you determine whether a hair transplant is a viable choice for your hair restoration journey.

Understanding Alopecia
Alopecia is a broad term for hair loss that can occur for various reasons. The most common types include:
- Androgenetic Alopecia (Male and Female Pattern Baldness): A hereditary condition that leads to gradual thinning of hair.
- Alopecia Areata: An autoimmune disorder where the immune system attacks hair follicles, causing patchy hair loss.
- Scarring Alopecia: A rare condition where inflammation destroys hair follicles, leading to permanent hair loss.
- Telogen Effluvium: Temporary hair loss caused by stress, illness, or hormonal changes.
What is a Hair Transplant?
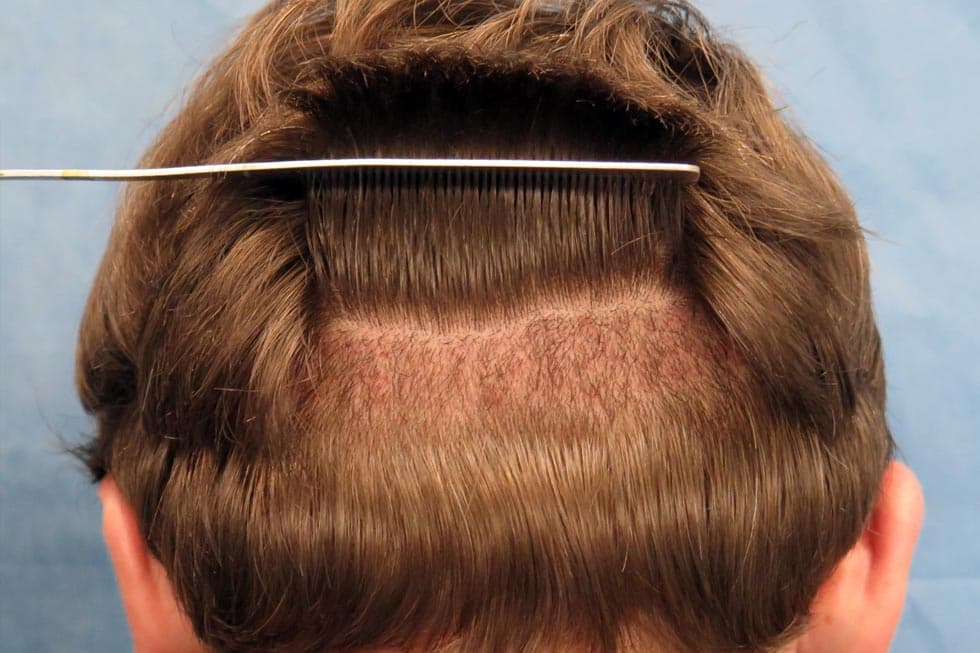
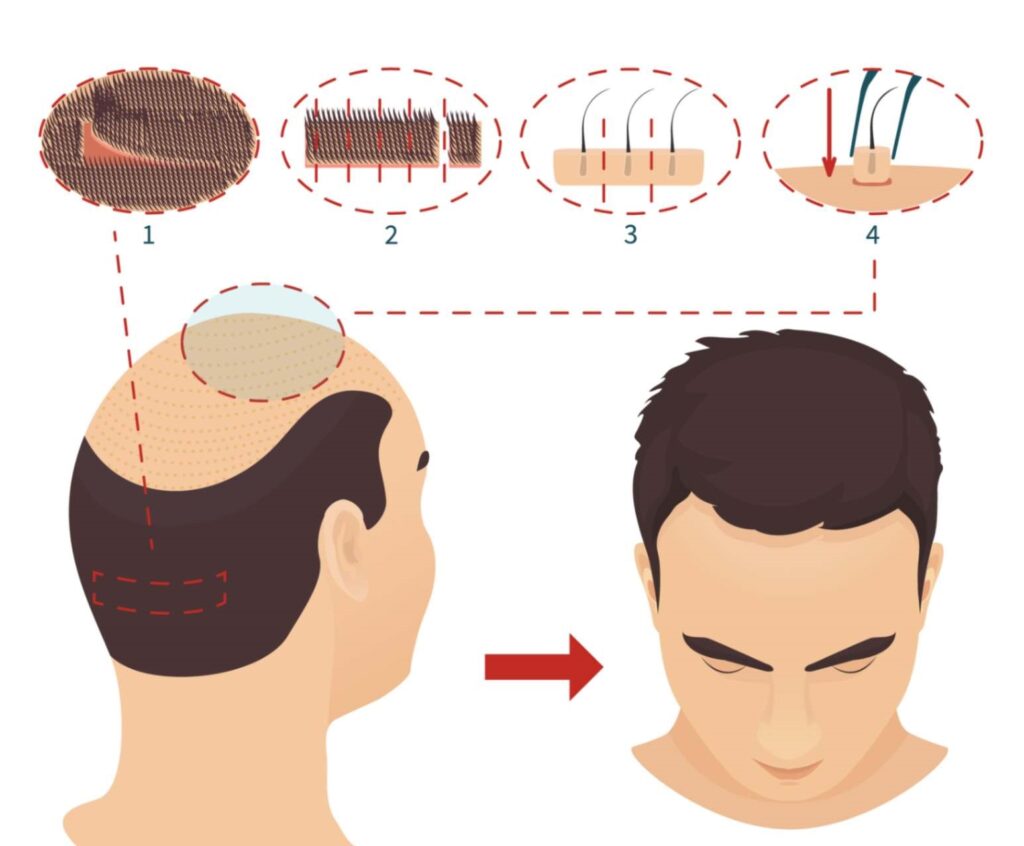
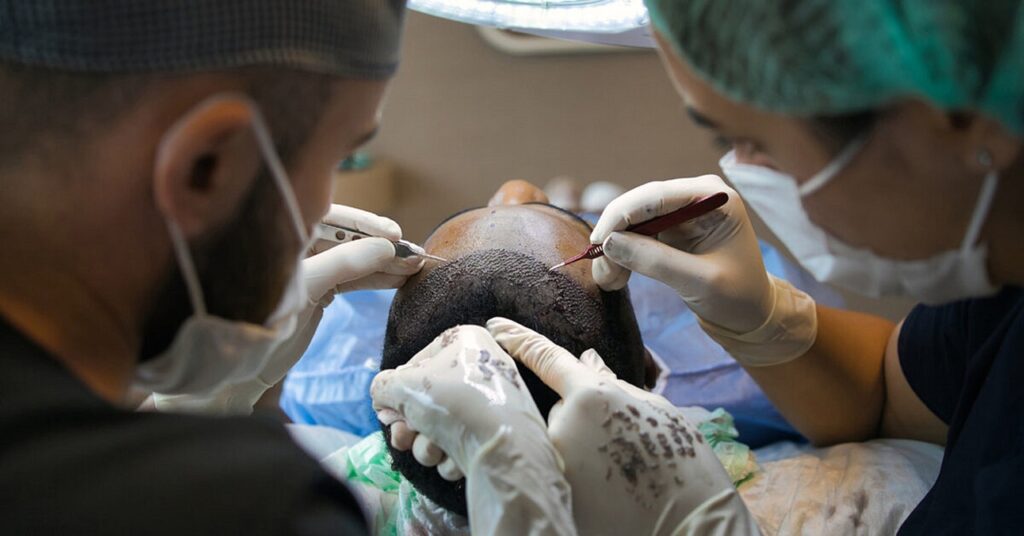
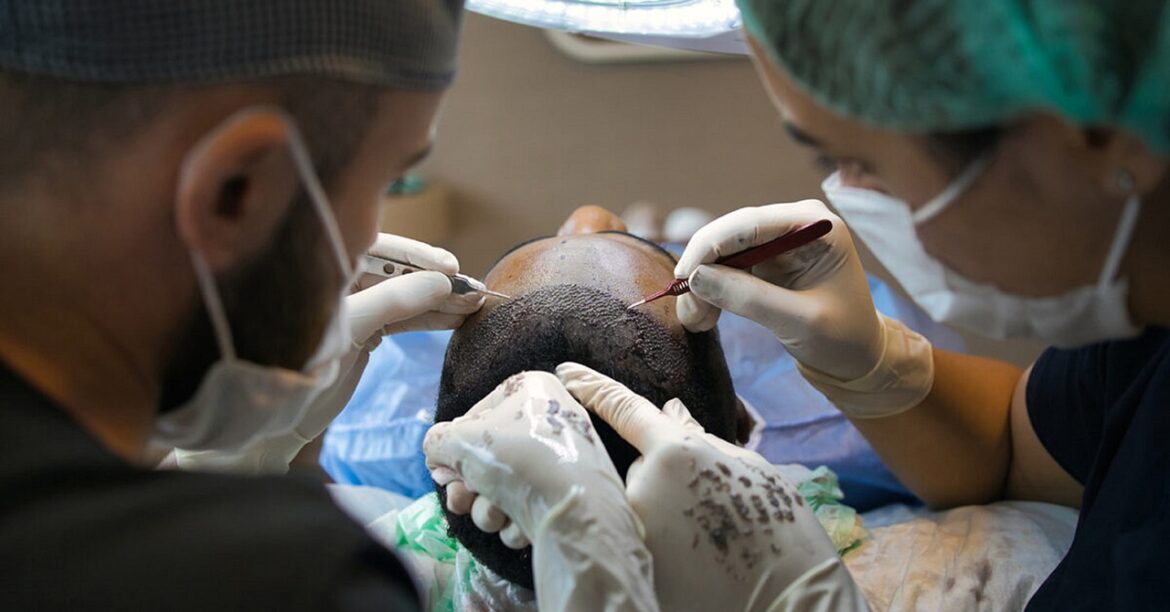
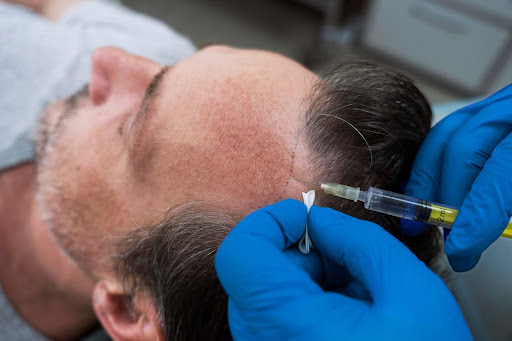
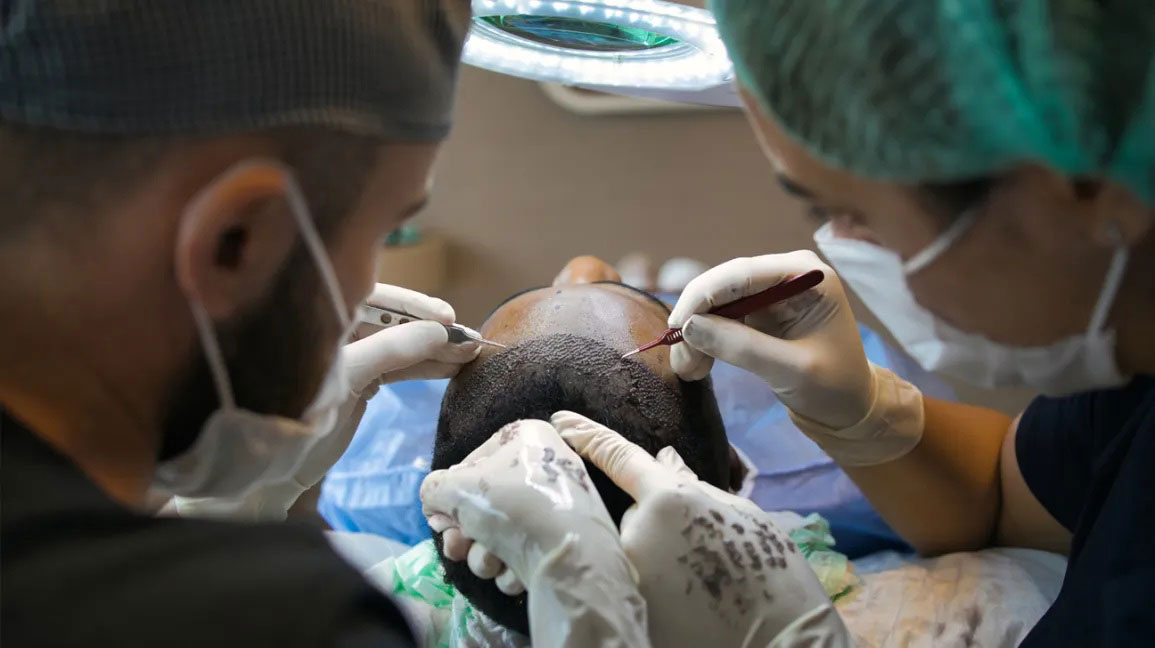
A hair transplant is a cosmetic surgery in which hair follicles are transplanted from a donor site (most often the back or sides of the head) to thinning or balding areas. The two major methods utilized are:
• Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT): The donor site skin strip carrying the hair follicles is transplanted into the recipient location.
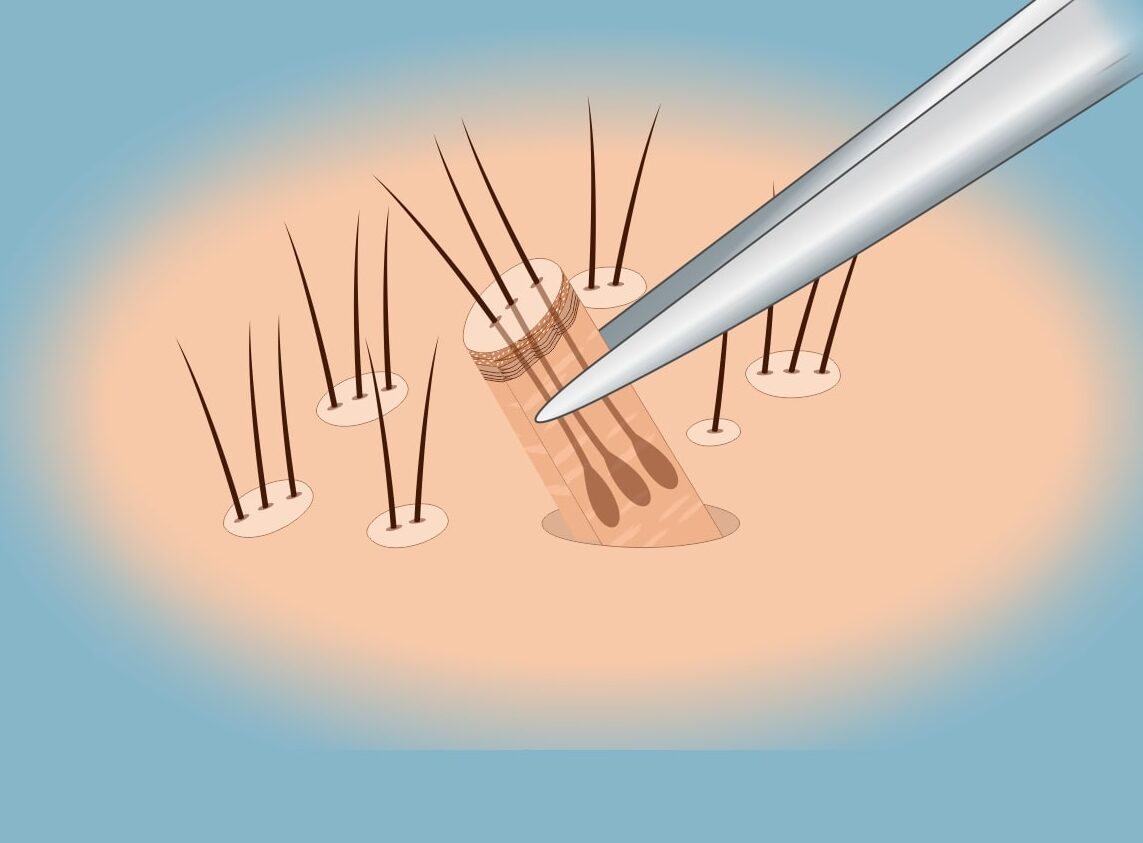
• Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE): Single hair follicles are removed and transplanted, causing minimal scarring.
Is Hair Transplant Suitable for Alopecia Patients?
Hair transplant success depends on the type of alopecia a patient has. Let’s examine the viability of hair transplants for different types of alopecia:

1. Androgenetic Alopecia
Best candidates: Hair transplants work best for patients with androgenetic alopecia, as they have a stable donor area where hair remains unaffected. If the patient has adequate donor hair, a hair transplant can provide long-lasting results.
2. Alopecia Areata
Limited success: Since alopecia areata is an autoimmune condition, transplanted hair may also be affected by the immune system, leading to unpredictable results. In most cases, dermatologists do not recommend hair transplants for alopecia areata patients unless the condition is stable for several years.
3. Scarring Alopecia
Good option: Scarring alopecia leads to permanent hair loss due to inflammation and follicular damage. Transplants in scarred areas have a lower success rate, as the blood supply to the area is compromised. However, with proper treatment and controlled inflammation, hair transplants can achieve a good success rate. Treatment with medication to control inflammation is necessary before considering a transplant.
4. Telogen Effluvium
Less recommended: This type of hair loss is temporary and often reversible once the underlying cause is addressed. A hair transplant is not needed in such cases, as hair usually regrows on its own.
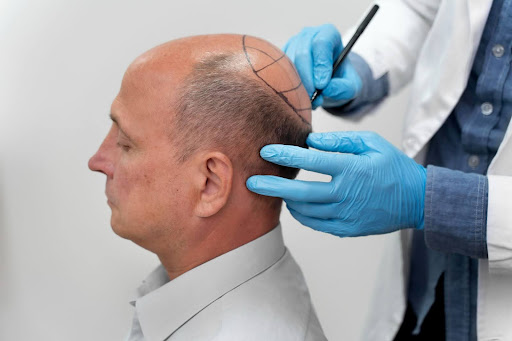
Factors to Be Addressed Prior to a Hair Transplant
Dermatologists consider several factors before a patient undergoes a hair transplant, such as:
- The stability of hair loss: Hair transplants work best with patients who have stable patterns of hair loss.
- The quality of the donor area: Enough good-quality hair needs to be available in the donor area for successful transplantation.
- The patient’s overall health: Diseases such as diabetes, autoimmune disorders, or unhealthy scalp condition may influence the success of the procedure.
- Realistic expectations: Hair transplants enhance hair density but cannot restore hair to its original volume.
Alternative Treatments for Alopecia

For patients who may not be suitable candidates for a hair transplant, other treatments are available, including:
• Medications: Minoxidil and finasteride can slow hair loss and promote regrowth.
• Mesotherapy & Exosome Therapy: These advanced treatments deliver growth factors and nutrients directly to the scalp to promote hair regeneration.
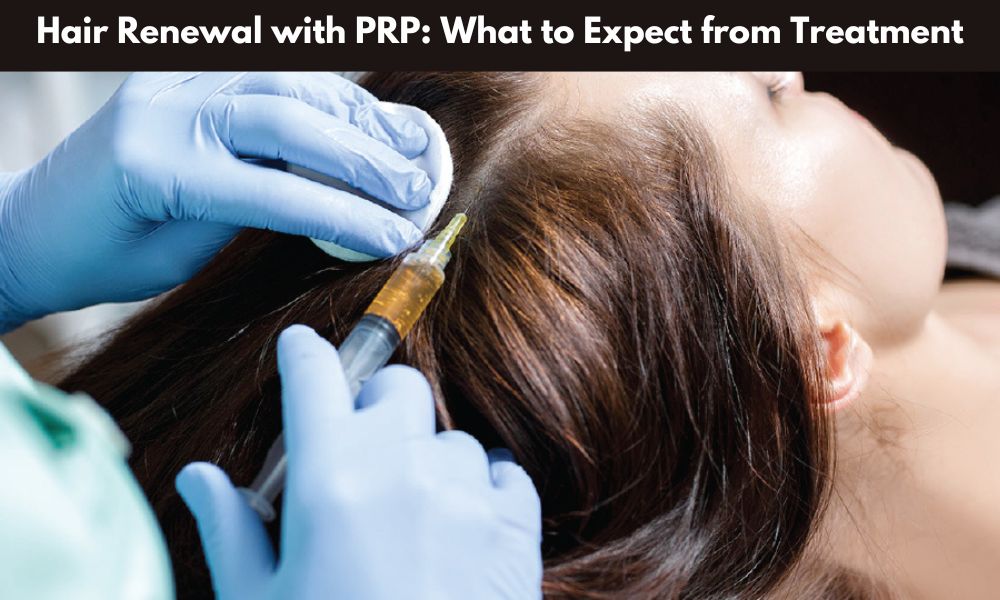
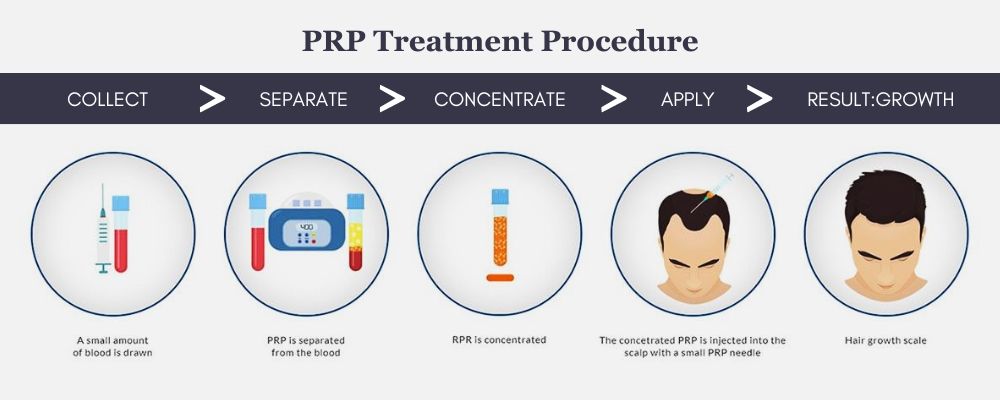
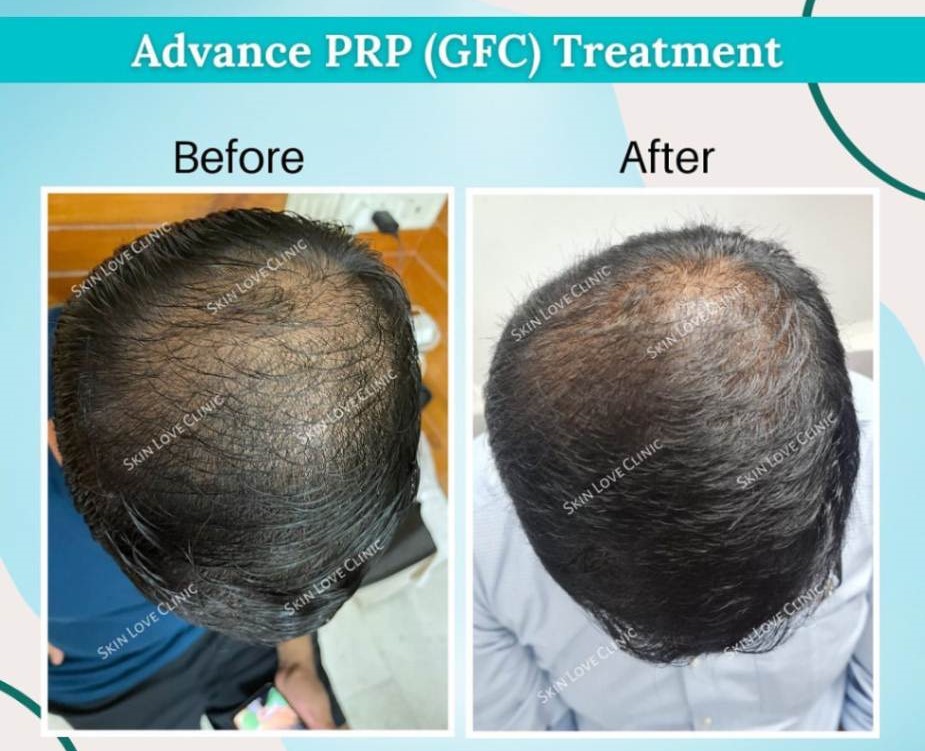
• Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy: Injecting platelets from the patient’s blood into the scalp to stimulate hair growth.
• Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT): A non-invasive treatment that promotes hair growth.
• Diet and Lifestyle Management: A well-balanced diet rich in protein and antioxidants, along with stress management and proper hair care, can support hair health.
Conclusion:
Hair transplants can be a viable solution for some alopecia patients, especially those with androgenetic alopecia. However, it is not suitable for all types of alopecia. A thorough evaluation by a dermatologist is essential to determine the best treatment plan. If you are experiencing hair loss, consult a specialist at SkinTown Clinic to explore the most effective options for your condition.