Psoriasis is a complex and often misunderstood skin condition affecting millions of people worldwide. Despite its prevalence, there are many misconceptions and a lack of understanding about this complex disease. As a Dermatologist it’s essential to provide comprehensive information to help patients better manage their condition. This blog aims to offer a comprehensive overview of psoriasis, including its symptoms, causes, and available treatments.
What is Psoriasis?
Psoriasis is an autoimmune condition that leads to the rapid accumulation of skin cells, resulting in the formation of thick, scaly patches on the skin’s surface. These patches are typically red, inflamed, and covered with silvery scales. Psoriasis can vary in severity, from localized patches to widespread skin coverage. The condition commonly affects areas such as the scalp, elbows, knees, and lower back.
Symptoms of Psoriasis
The psoriasis symptoms can differ from person to person, but common signs include:
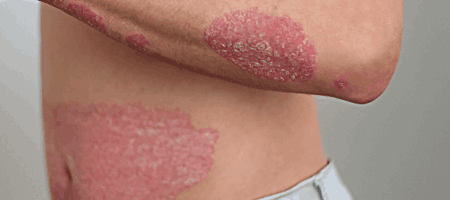
- Red patches of skin: Often covered with thick, silvery scales.
- Dry, cracked skin: Which may bleed or itch.
- Itching, burning, or soreness: In and around the affected areas.
- Thickened or ridged nails: Psoriasis can also affect fingernails and toenails, causing them to become thick and discolored.
- Swollen and stiff joints: Some individuals with this condition also develop psoriatic arthritis, leading to joint pain and swelling.
Causes of Psoriasis
What causes psoriasis remains unknown, but it is believed to be related to an immune system problem with T cells and other white blood cells, called neutrophils, in the body. Normally, T cells travel throughout the body to detect and fight off foreign substances, such as viruses or bacteria. In this disease, these T cells mistakenly attack healthy skin cells.
Factors that may trigger psoriasis include:
- Genetics: Psoriasis often runs in families. If one parent has this condition, there’s a 10% chance of a child developing it; if both parents have it, the chance increases to 50%.
- Infections: Such as strep throat or skin infections.
- Stress: Stress can impact the immune system and trigger psoriasis flare-ups.
- Season: Winter season can worsen symptoms, while summer can improve them.
- Injury to the skin: Such as a cut, scrape, insect bite, or sunburn (known as the Koebner phenomenon).
- Certain medications: Including lithium, antimalarials, and beta-blockers.
- Lifestyle factors: Such as smoking and heavy alcohol consumption.
Treatments for Psoriasis
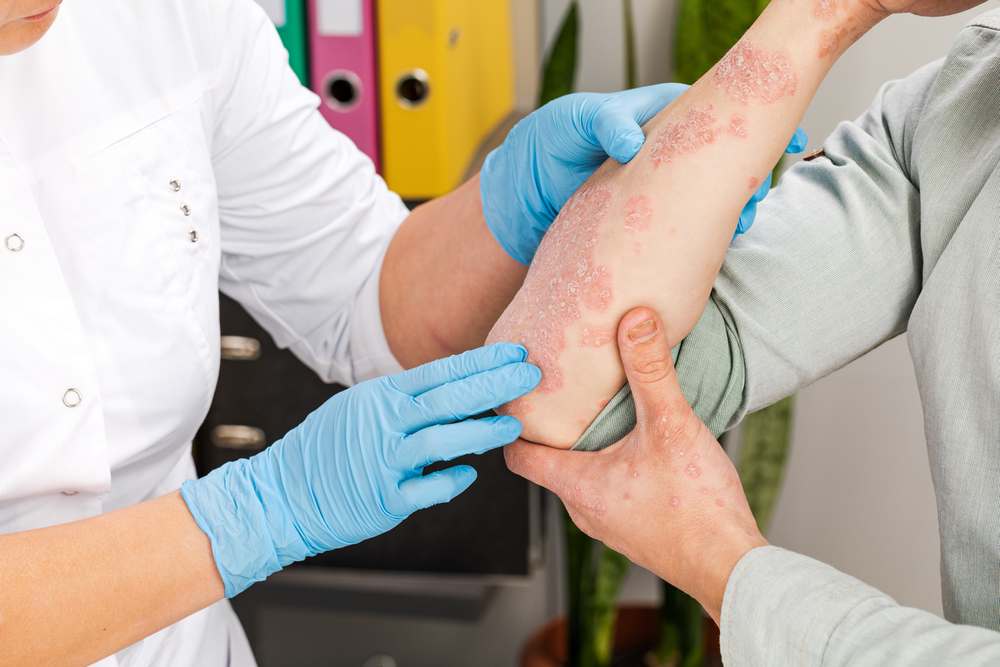
While there is no cure for this condition, several treatment options can help control symptoms and improve quality of life. The choice of psoriasis treatment depends on the type and severity of the this skin disease and the areas of skin affected.
- Topical Treatments: These are applied directly to the skin and are often the first line of defense. Common topical treatments include:
- Phototherapy: This involves exposing the skin to ultraviolet light under medical supervision. Types of phototherapy include:
- UVB Phototherapy: Uses UVB light to penetrate the skin and slow the growth of affected skin cells.
- PUVA Therapy: Combines a drug called psoralen with UVA light to treat severe psoriasis.
- Systemic Treatments: These are oral or injected medications that work throughout the entire body. They are typically used for more severe cases. Examples include:
- Methotrexate: Reduces the production of skin cells and suppresses inflammation.
- Cyclosporine: Suppresses the immune system.
- Biologics: Target specific parts of the immune system (e.g., TNF-alpha inhibitors, IL-12/23 inhibitors).
- Lifestyle and Home Remedies: These can also play a crucial role in managing psoriasis symptoms:
- Moisturizing regularly: Keeps the skin hydrated and reduces itching and scaling.
- Bathing with oils and salts: Can soothe irritated skin.
- Avoiding triggers: Identifying and avoiding personal triggers such as stress, trauma, alcohol, and smoking.
- Corticosteroids: Reduce inflammation and slow the rapid production of skin cells.
- Vitamin D analogs: Slow skin cell growth.
- Topical retinoids: Normalize DNA activity in skin cells.
- Calcineurin inhibitors: Reduce inflammation and plaque build-up.
Conclusion:
Understanding psoriasis is the first step toward effectively managing this chronic condition. By recognizing the symptoms, knowing the causes, and exploring various treatment options, patients can better control their psoriasis and lead more comfortable lives. At Skin Town Clinic, Dr. Bhushan Bawankar is a Certified Dermatologist & Psoriasis Specialist in Dadar, Mumbai, with extensive experience, providing accurate and compassionate care is essential in helping patients navigate their journey with psoriasis. If you or someone you know is struggling with this condition, don’t hesitate to seek professional medical advice and explore the best treatment plan for your specific needs.

